Hot News

iPhone 16 Launch in Indonesia
Apple's iPhone 16 is finally making its way to Indonesia. Packed with cutting-edge features, improved battery life, and a more powerful A18 chip, the iPhone 16 promises to redefine the smartphone experience.
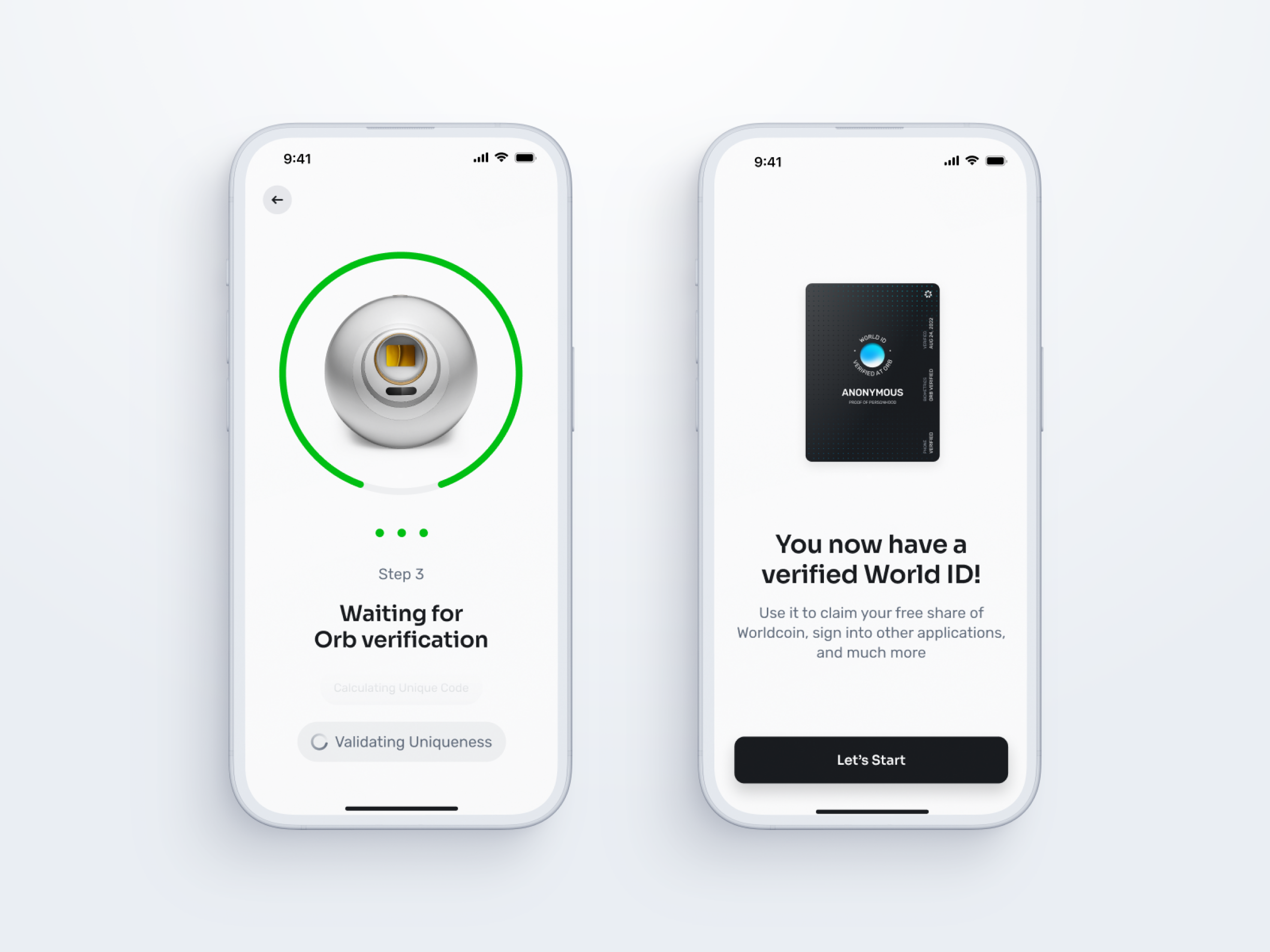
World App Coin in Indonesia
The World App Coin (WAC), a new cryptocurrency, has recently made its debut in Indonesia. This digital currency promises to bring innovation in financial transactions for the modern era.
